North Korean hackers are reportedly targeting cryptocurrency professionals using new malware called “PylangGhost” through fake job interviews, according to Cisco Talos on June 20th.
The incident highlights ongoing risks in the crypto sector from state-sponsored actors, raising security concerns particularly on individual-level asset protection.
PylangGhost Malware Posing as Job Offers Targets Crypto Sector
North Korean hacking group “Famous Chollima” has deployed a Python RAT known as “PylangGhost” to target cryptocurrency professionals. These attacks mimic job offers from prominent firms like Coinbase and Uniswap, employing social engineering tactics to gain trust.
The malware campaign aims to capture sensitive information, including user credentials and cryptocurrency wallet details. Security experts anticipate increased threats as attackers exploit recruitment-related activities to infringe crypto industry safeguards.
The current situation has drawn no official statements from affected companies or regulatory bodies. Despite notable threat levels, no reports of asset loss have emerged, maintaining a continued focus on preventative measures within the industry.
Historical Patterns and Security Measures in Focus
Did you know? The Famous Chollima group, involved since at least 2018, has previously executed similar high-profile attacks, notably impacting Ronin Bridge and KuCoin, reflecting persistent strategies.
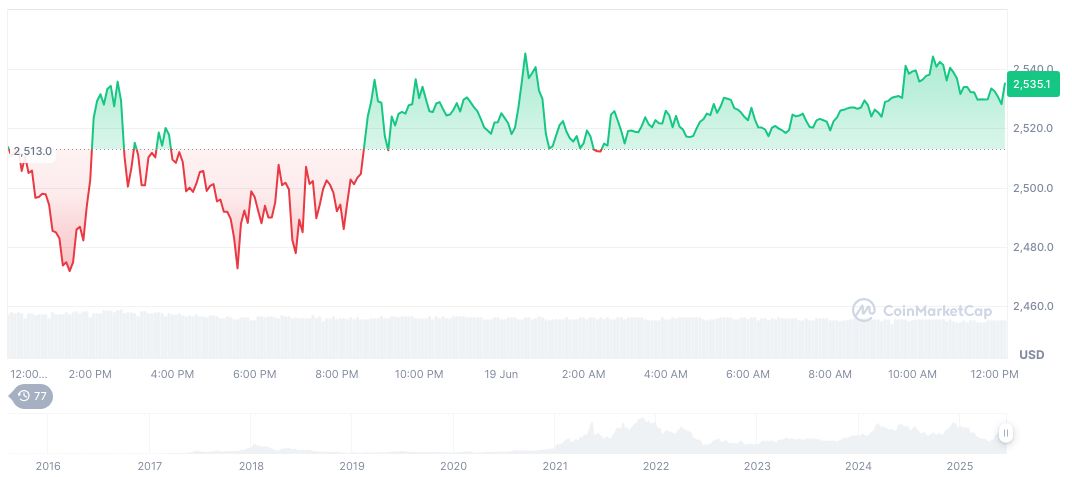
Ethereum (ETH) trades at $2,521.45, with a market capitalization of $304.39 billion, accounting for 9.37% of the market. Notably, its 24-hour trading volume decreased by 36.73%, reflecting a quieter trading session. In two months, ETH increased by 52.98%, according to CoinMarketCap.
Experts from the Coincu research team project that such cyber threats may lead to stricter security protocols in hiring processes across the blockchain industry. The ongoing sophistication of attacks underlines the necessity for enhanced cybersecurity measures to shield individual and organizational interests.